- Bootable USB Creators
- Database Management Software
- Remote Desktop Software
- Miscellaneous Software
- IDE Software
- CAD Software
- VPN Software
- Messaging Software
- Download Managers
- GIS Software
- Web Browsers
- PDF Editors
- PDF Readers
- 3D Modeling Software
- Image Editing Software
- Video Playing Software
- Virtualization Software
- Backup Software
- Browser Plug-ins
- Live Stream Software
- Disk Formatting Software
- File Managers
- 3D Model Viewing Software
- 2D Animation Software
- Racing Games
- Mouse Cursor Software
- Android Emulators
- File Compression Software
- Programming Languages
- Digital Art Software
Sysmon 15.11
| Narxi | Ozod |
| Versiya | 15.11 |
| Ishlab chiqarilish sanasi | December 18, 2023 |
| Nashriyotchi | Mark Russinovich - https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals |
| Nashriyot tavsifi | |
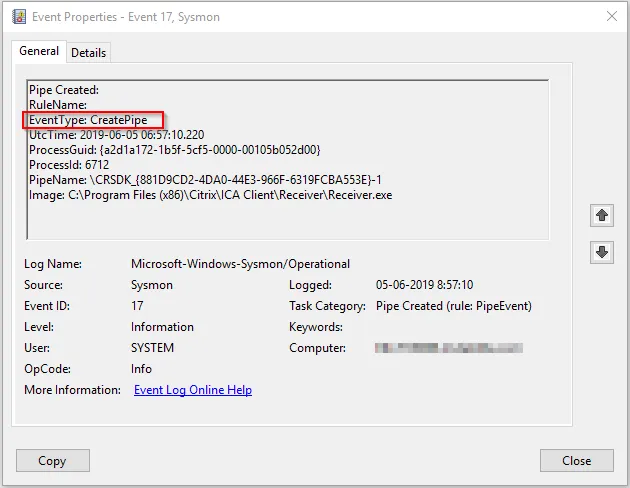
System Monitor (Sysmon) is a Windows system service and device driver that, once installed on a system, remains resident across system reboots to monitor and log system activity to the Windows event log. It provides detailed information about process creations, network connections, and changes to file creation time. By collecting the events it generates using Windows Event Collection or SIEM agents and subsequently analyzing them, you can identify malicious or anomalous activity and understand how intruders and malware operate on your network.
Note that Sysmon does not provide analysis of the events it generates, nor does it attempt to protect or hide itself from attackers.
Overview of Sysmon Capabilities
Sysmon includes the following capabilities:
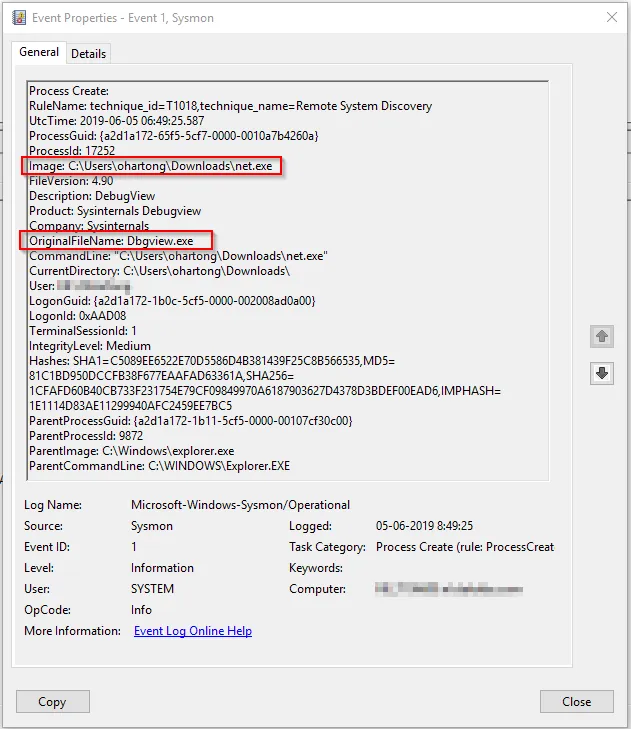
- Logs process creation with full command line for both current and parent processes.
- Records the hash of process image files using SHA1 (the default), MD5, SHA256 or IMPHASH.
- Multiple hashes can be used at the same time.
- Includes a process GUID in process create events to allow for correlation of events even when Windows reuses process IDs.
- Includes a session GUID in each event to allow correlation of events on same logon session.
- Logs loading of drivers or DLLs with their signatures and hashes.
- Logs opens for raw read access of disks and volumes.
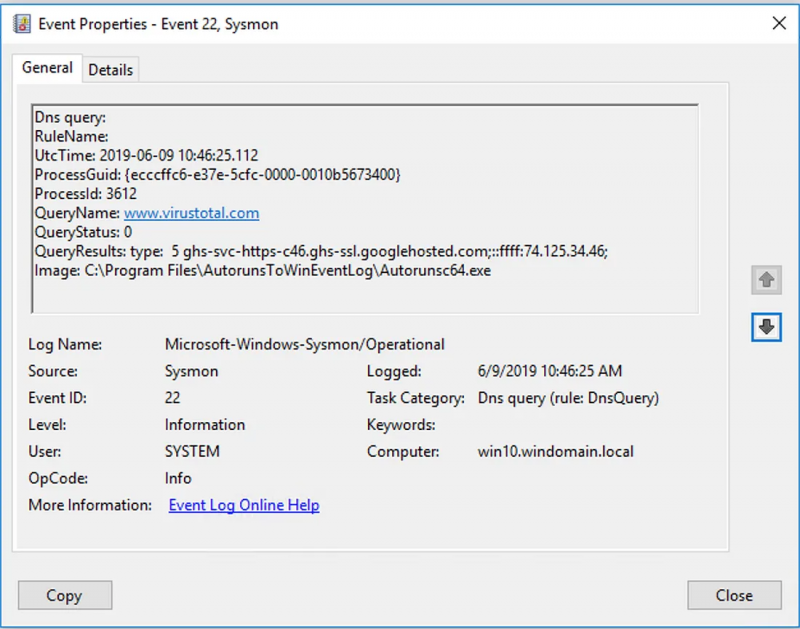
- Optionally logs network connections, including each connection’s source process, IP addresses, port numbers, hostnames and port names.
- Detects changes in file creation time to understand when a file was really created. Modification of file create timestamps is a technique commonly used by malware to cover its tracks.
- Automatically reload configuration if changed in the registry.
- Rule filtering to include or exclude certain events dynamically.
- Generates events from early in the boot process to capture activity made by even sophisticated kernel-mode malware.